Foundation Retaining Wall Shoring: Ensuring Structural Stability
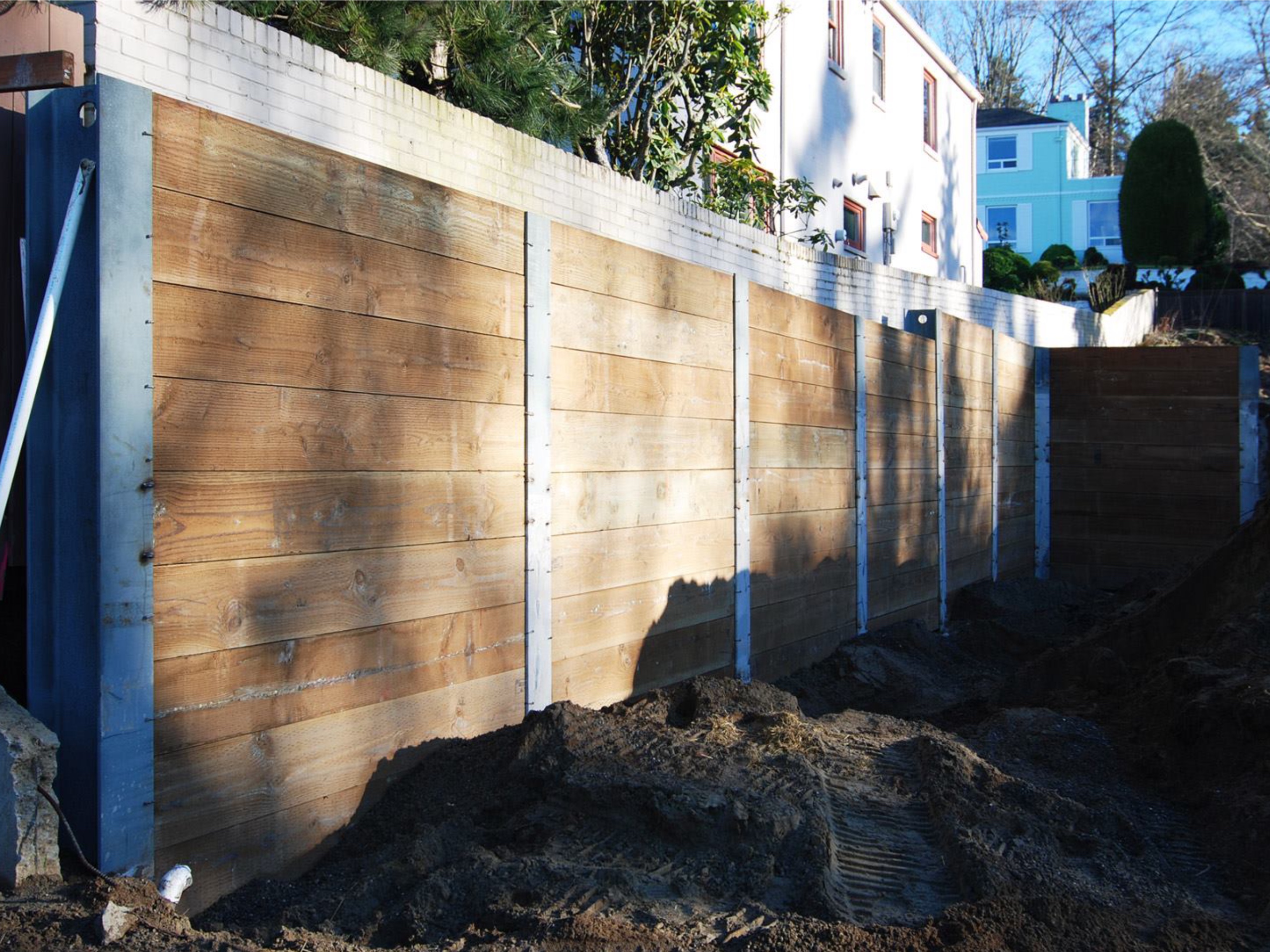

Foundation retaining wall shoring is a critical process in construction and engineering, involving the reinforcement and stabilization of retaining walls to prevent soil movement and ensure structural integrity. This technique is essential for maintaining the safety and longevity of structures adjacent to excavations or unstable terrains.
🔍 Understanding Retaining Wall Shoring
Shoring refers to the process of supporting a structure, trench, or excavation to prevent collapse. In the context of retaining walls, shoring provides lateral support to withstand earth pressures and maintain the wall's stability.
⚙️ Common Shoring Methods for Retaining Walls
Several techniques are employed to shore retaining walls, each selected based on site conditions, wall height, and project requirements:

Soldier Pile and Lagging
Common in block walls; indicates uneven settling or lateral soil pressure.

Soil Nailing
Involves inserting steel bars into pre-drilled holes in the slope or excavation face, which are then grouted to create a composite mass resisting soil movement. A facing, often shotcrete, is applied for additional support.

Helical Tieback Anchors
Utilizes screw-like anchors installed into the soil behind the retaining wall to provide lateral support. These anchors can be tensioned immediately, offering quick stabilization.
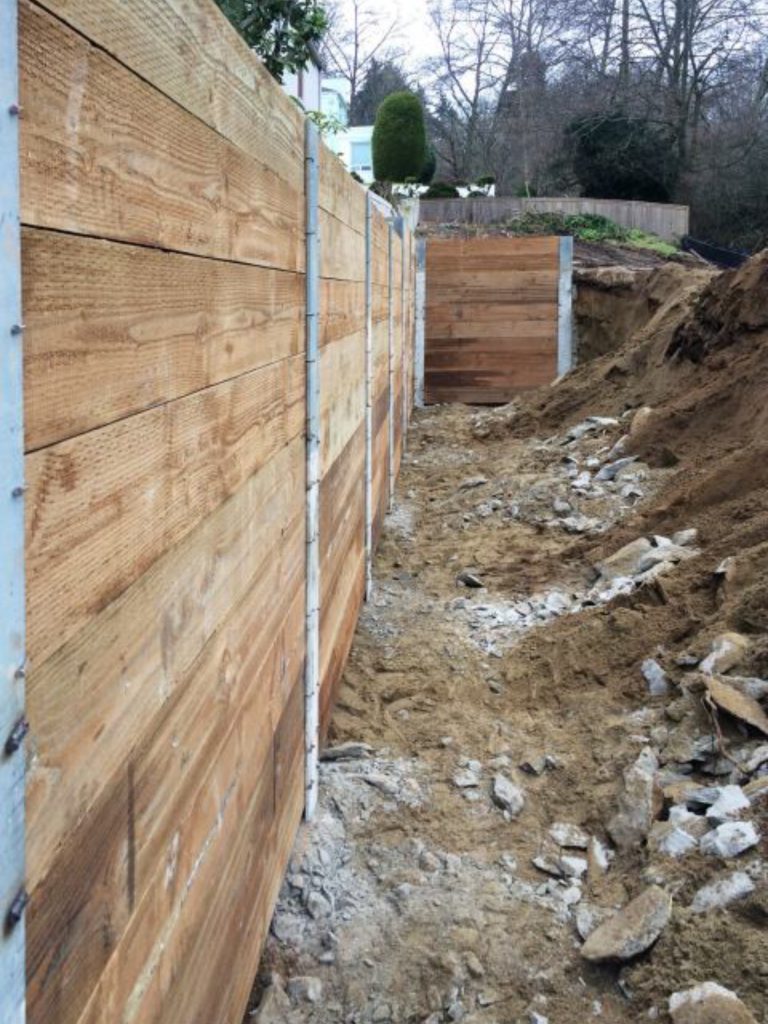
Sheet Piling
Involves driving interlocking sheets of steel, vinyl, or wood into the ground to form a continuous barrier against soil movement. This method is effective in soft soils and tight spaces.

Braced Excavation (Strutting and Bracing)
Employs horizontal or diagonal supports (struts and braces) between opposing walls of an excavation to prevent collapse during construction.
🛠️ Design Considerations in Retaining Wall Shoring
Effective shoring design requires careful evaluation of several factors:

Soil Characteristics
Understanding soil type, cohesion, and angle of internal friction is crucial for determining earth pressures and selecting appropriate shoring methods.

Wall Height and Load
The height of the retaining wall and any additional loads (e.g., nearby structures or vehicular traffic) influence the choice of shoring technique and structural specifications.

Drainage and Water Table
Proper drainage systems are essential to prevent water buildup behind the wall, which can increase pressure and reduce stability.

Construction Sequence and Site Constraints
The proximity of existing structures, property lines, and access limitations can affect the feasibility of certain shoring methods.

Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Adherence to local building codes and safety standards is mandatory to ensure the protection of workers and the public.
🏠 Applications of Retaining Wall Shoring
Shoring techniques are employed in various scenarios, including:

Deep Excavations
Providing support during the construction of basements, underground parking, and tunnels to prevent soil collapse.

Slope Stabilization
Reinforcing natural or man-made slopes to prevent landslides and erosion.

Infrastructure Projects
Supporting retaining walls in the construction of bridges, highways, and railways, ensuring stability in cut-and-fill operations.

Building Adjacent to Existing Structures
Safeguarding neighboring buildings during excavation by preventing soil movement that could undermine foundations.
Selecting the appropriate shoring method also involves evaluating environmental impact and cost-effectiveness:

Material Selection
Using sustainable materials and methods that minimize environmental disruption.

Construction Time and Labor
Efficient shoring techniques can reduce construction time and labor costs, contributing to overall project savings.

Long-Term Maintenance
Considering the durability and maintenance requirements of the shoring system to ensure long-term stability and cost efficiency.
🌍
Environmental and Economic Considerations
Foundation retaining wall shoring is a vital component in construction, ensuring the safety and longevity of structures by effectively managing soil pressures and preventing collapses.
A thorough understanding of various shoring methods, coupled with careful design and consideration of site-specific factors, is essential for successful implementation.
✅ Benefits of Foundation Retaining Wall Shoring
Why proper shoring is essential for your project:

Prevents Wall Failures and Soil Collapse
By stabilizing the wall and surrounding soil, shoring ensures that excavation doesn’t lead to catastrophic collapse or landslides.

Protects Surrounding Structures
Critical in urban or tight construction zones where neighboring buildings are close to excavated areas.

Allows for Safer & Deeper Excavations
Enables contractors to dig deeper for basements or infrastructure while keeping the work zone safe and structurally sound.

Reduces Settlement Risks
Minimizes ground movement that can cause uneven settlement or damage to structures, sidewalks, and roads nearby.

Meets Code and Engineering Standards
Professional shoring plans are designed to comply with all relevant building regulations and safety codes.
🧱 When Do You Need Retaining Wall Shoring?
You may need professional shoring services when:

There are visible signs of bowing, tilting, or cracking in a wall

You’re working in tight construction sites where excavation boundaries are limited

You're excavating next to an existing home, building, or sidewalk

Your site has soft, loose, or saturated soils

The retaining wall supports multiple levels or heavy loads

💬 FAQs About Foundation Retaining Wall Shoring
Wall shoring is a preventative or supportive structural technique used during construction or excavation to hold back soil. It’s different from wall repair, which addresses damage after it occurs. Shoring is about proactive support.
Yes. Shoring is especially important on hillsides or slopes where soil erosion and lateral pressure are highest. Tiebacks, soldier piles, or soil nails are often used for these areas.
Some methods, like tiebacks or soil nails, may require drilling or access behind the wall. Others, like internal bracing or helical anchors, can be installed with minimal excavation, depending on the system used.
It can be both. Shoring may be temporary during construction, or designed as a permanent structural element in challenging soil conditions.
Most residential and light commercial shoring projects take about a week, depending on wall height, soil type, and system used.
Costs vary depending on the site, wall size, and method used. Helical or anchor-based systems are often more cost-effective long term due to reduced excavation and quicker installation.
Homes Secured
Successful Projects
Years of Experience
Specialized Services
Trusted Locally. Built Personally.
Proudly serving Colorado with foundation solutions tailored to your home.
© 2025 The Foundation Guys. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility

Book Your Appointment Today!
Complete this form to have a The Foundation Guys representative reach out to you today.
By clicking submit, you agree to receive marketing and informational calls and texts, including autodialed or prerecorded calls/texts, to the telephone numbers that you provide, including any mobile number, from or on behalf of The Foundation Guys. Consent is not a condition of purchase. Message and frequency may vary. Message and data rates may apply. Text HELP for help and STOP to unsubscribe. For more information, please review our Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions.
